Researchers say the interstellar visitor 3I/ATLAS is a natural comet, not an extraterrestrial spacecraft. New radio observations timed for the object's closest approach to Earth found no signs of artificial radio transmissions, reinforcing NASA's repeated statements since the object was discovered.
Key observation: An international team associated with the Breakthrough Listen initiative used the Green Bank Telescope in West Virginia to target 3I/ATLAS on Dec. 19, 2025 — the day it passed closest to Earth — and detected no measurable technosignatures (artificial radio emissions). The non-detection led the team to conclude the object shows no evidence of being technological, though the paper describing the observations has not yet been peer-reviewed.
What We Know About 3I/ATLAS
3I/ATLAS was confirmed in July 2025 as the third known object to originate from outside our solar system. At discovery NASA reported its speed at roughly 137,000 mph, and trajectory analysis shows it likely formed around another star and was ejected into interstellar space. Its incoming direction is roughly from the region of the constellation Sagittarius.
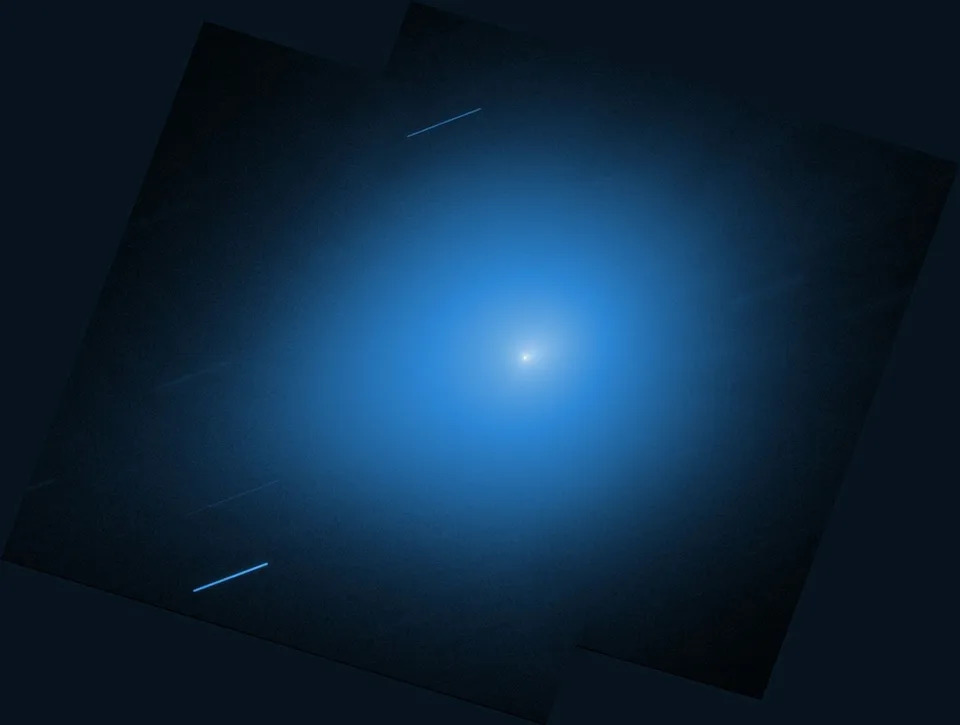
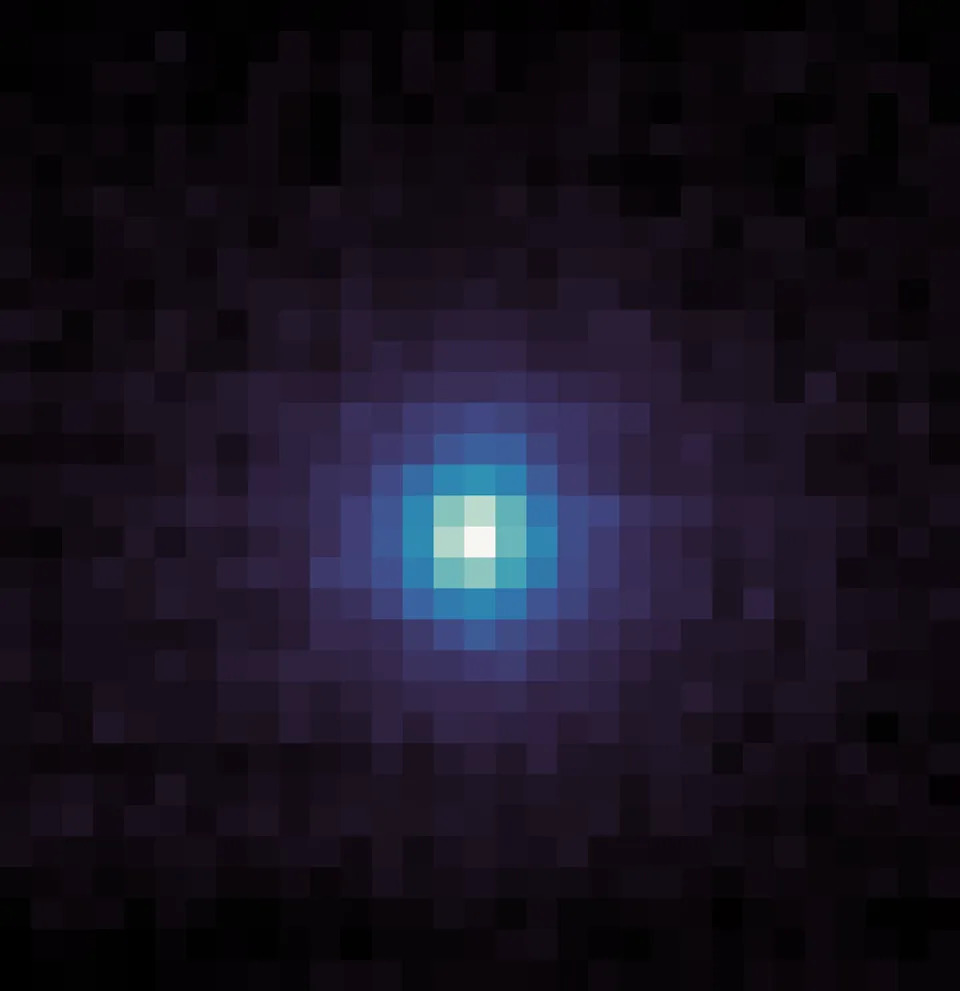
Estimates of the object's size vary. The European Space Agency suggested a broad range from a few hundred feet to a few miles across. Hubble Space Telescope observations constrained the diameter of the comet’s solid, icy nucleus to roughly 1,400 feet up to about 3½ miles.
Unlike solar-bound comets, 3I/ATLAS follows a hyperbolic path and will continue back into interstellar space after its brief passage through our system. At closest approach on Dec. 19, 2025, it passed about 170 million miles from Earth — roughly twice the Earth–Sun distance and many hundreds of times the Earth–Moon separation — so it posed no threat to our planet.
Conspiracy Claims and Scientific Response
The object's interstellar origin and unusual orbit prompted public speculation, including suggestions from some that it might be artificial. Harvard astrophysicist Avi Loeb has argued such possibilities should be considered, and he has urged broader, longer-term monitoring. Loeb has also acknowledged the object is "most likely a comet of natural origin," but has not completely ruled out other explanations.
"It is unclear whether one should expect a technological object to transmit radio signals to its senders," Loeb wrote, noting that a comprehensive search would monitor the object from many directions over an extended period.
NASA officials have repeatedly dismissed the alien-technology interpretation. In an October 2025 social-media exchange then-Acting Administrator Sean Duffy wrote: "No aliens. No threat to life here on Earth." Nicola Fox, associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, told reporters in November 2025 that scientists had not observed any technosignatures or any other sign indicating the object is anything other than a comet.
Why This Matters
The Breakthrough Listen non-detection does not prove that all possible non-natural scenarios are impossible — it only shows there were no detectable artificial radio emissions during the targeted observations. Still, the combined evidence (trajectory, brightness and composition estimates, lack of radio technosignatures, and NASA analyses) strongly supports the conclusion that 3I/ATLAS is a natural interstellar comet. It remains a scientifically valuable object for studying materials from another star system.
NASA has released additional images and maintains public tracking resources, including the "Eyes on the Solar System" simulation and catalog entries at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, for anyone who wants to follow 3I/ATLAS's path and data.
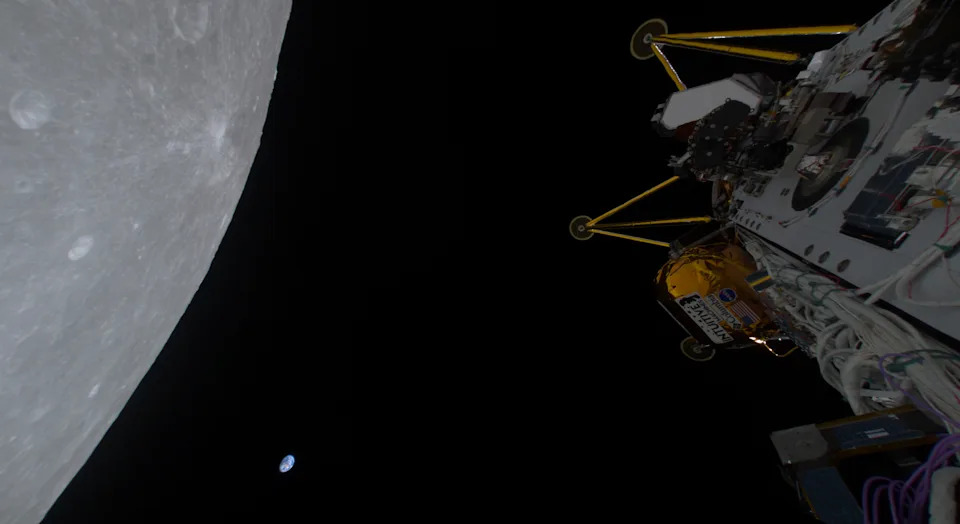
Athena, the lunar lander on Intuitive Machines' IM-2 mission, captured this image of the moon's surface with Earth seen in the distance ahead of a March 6 landing attempt. While the lander was the second U.S. vehicle to reach the moon within a week, it ultimately landed on its side, which hindered much of its mission.
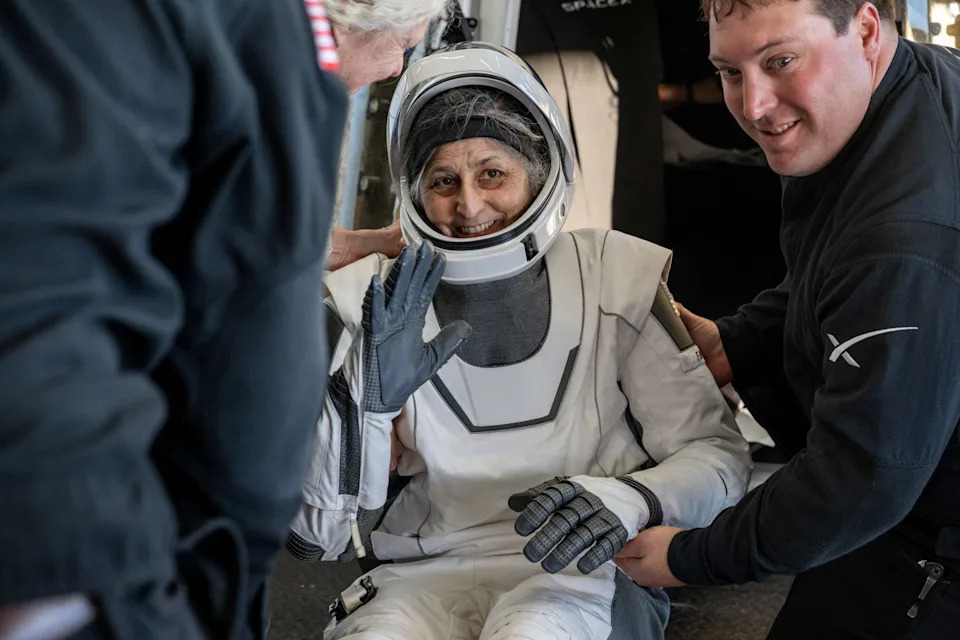
NASA astronaut Suni Williams is helped out of a SpaceX Dragon spacecraft March 18 following a return to Earth after a nine-month stay at the International Space Station. She and NASA astronaut Butch Wilmore crewed the Boeing Starliner, which had launched in June 2024 on a failed test flight that was meant to return them to Earth a few days later.
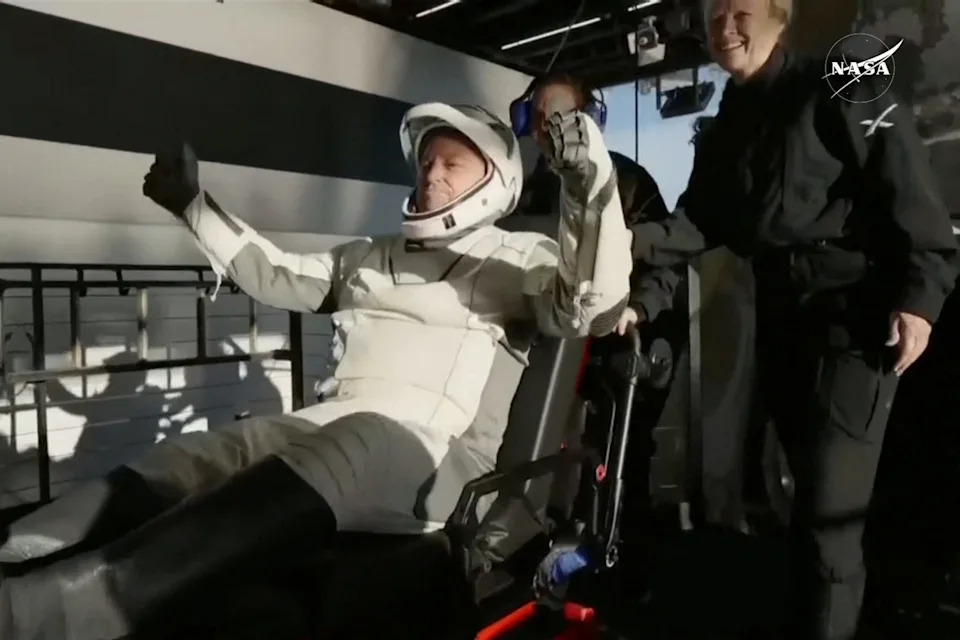
Butch Wilmore reacts after he and Suni Williams and two other astronauts splashed down March 18 in a Crew Dragon space capsule following their return to earth from the International Space Station off the coast of Florida. The astronauts' extended stay at the orbital outpost dominated the news cycle for months.
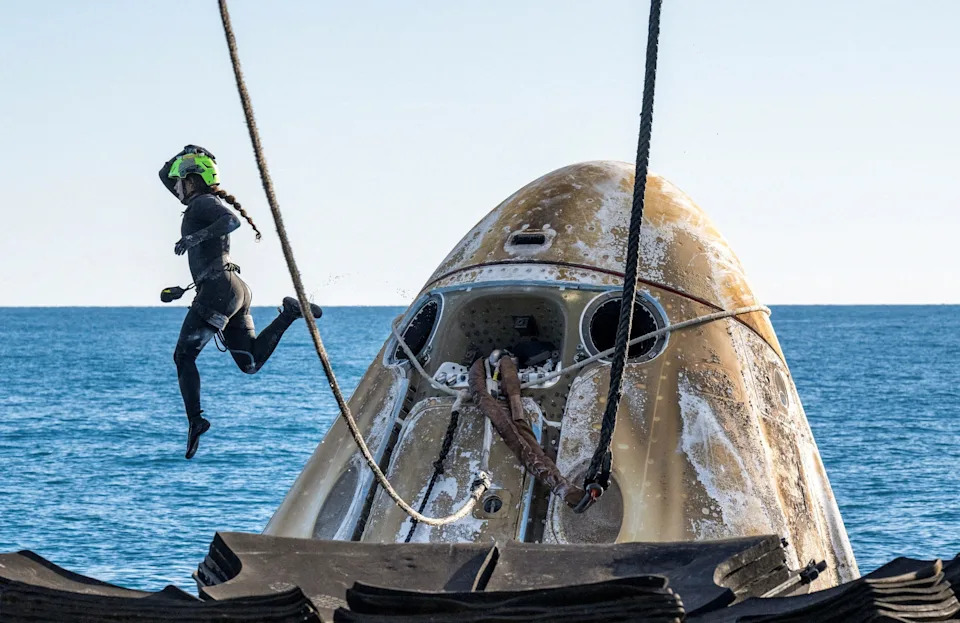
A SpaceX support team member is seen airborne while working to lift the SpaceX Dragon capsule that returned the Starliner astronauts and two others onto a recovery vehicle following its landing off the coast of Florida.
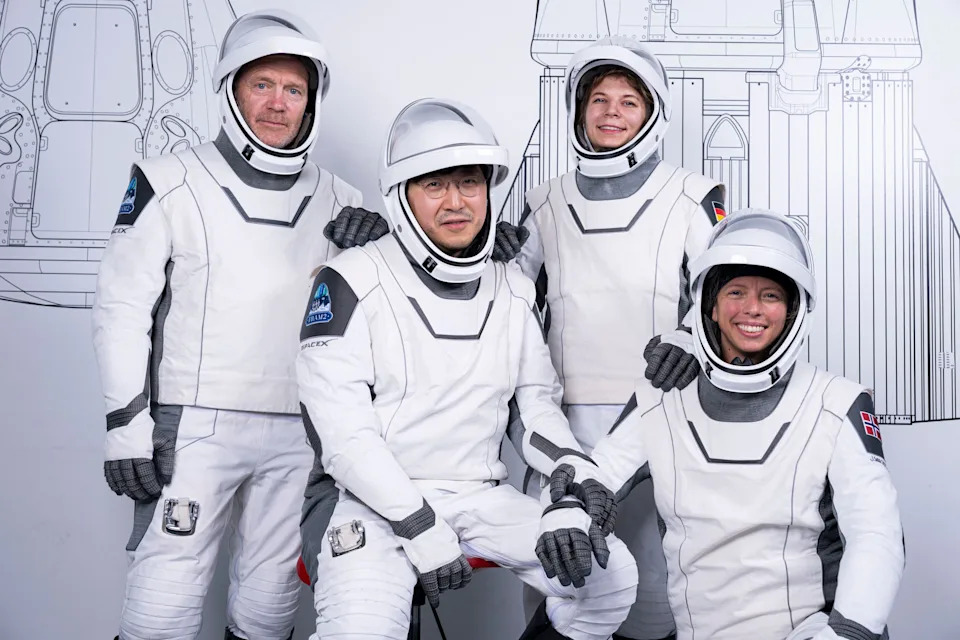
This picture shows the crew of a privately-funded mission known as Fram2, from left to right, mission specialist and medical officer Eric Philips, mission commander Chun Wang, pilot Rabea Rogge and vehicle commander Jannicke Mikkelsen on March 19, 2025 in Hawthorne, California. Launched March 31 from Florida using a SpaceX Dragon capsule, the mission became t first ever human spaceflight over the Earth's polar regions.
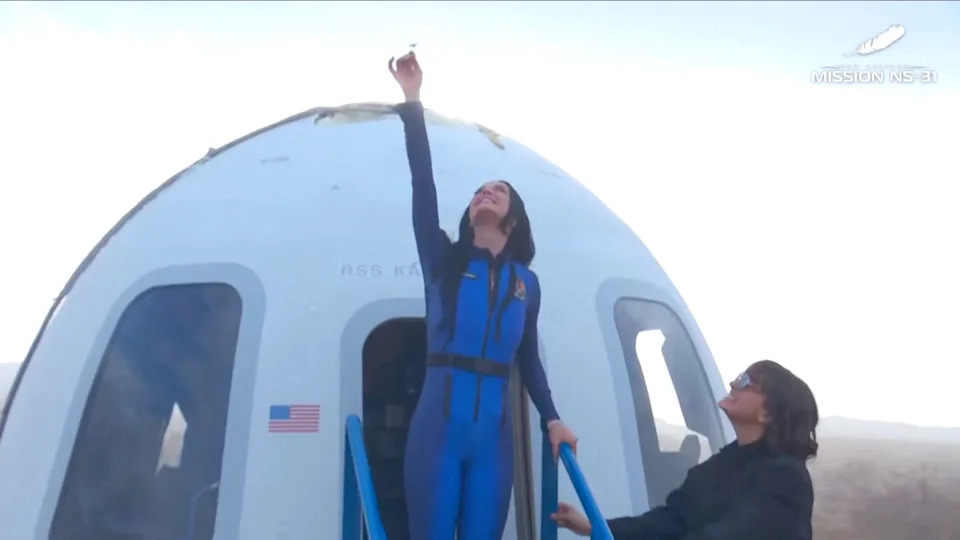
Pop musician Katy Perry emerges April 14 from Blue Origin's New Shepard capsule in West Texas following a brief flight to the edge of space. Perry was part of an all-women crew that also included broadcast journalist Gayle King that took the ride from Blue Origin's facility called Launch Site One. The high-profile launch attracted plenty of headlines and even drew some backlash from those who viewed the mission as a wasteful publicity stunt.
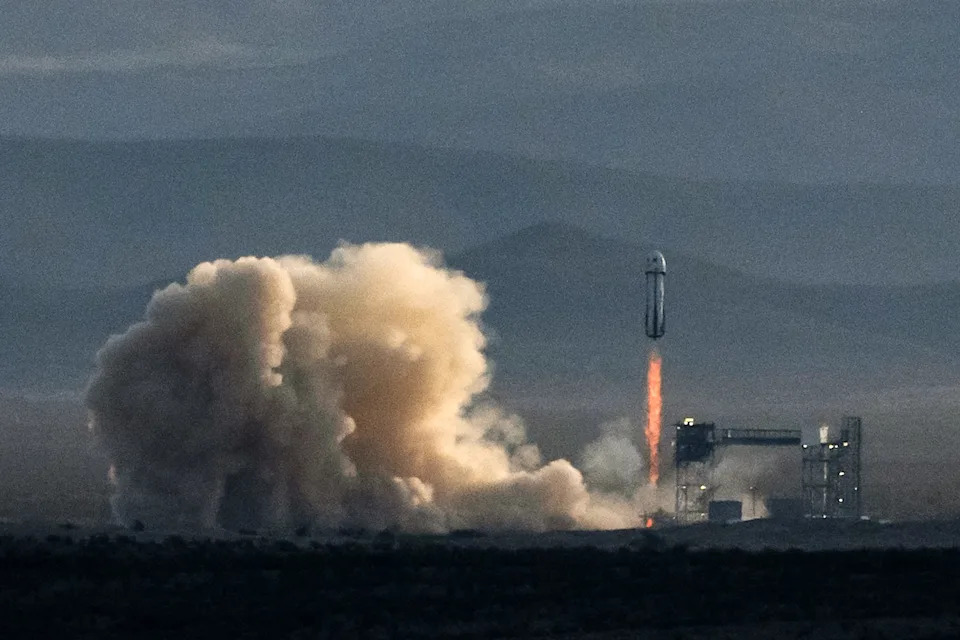
Blue Origin's New Shepard rocket carrying astronauts Aisha Bowe, Amanda Nguyen, Kerianne Flynn, Gayle King, Katy Perry, and Lauren Sanchez lifts off April 14 from Launch Site One near Van Horn, Texas. Blue Origin has since launched five more human spaceflights on the New Shepard in 2025.
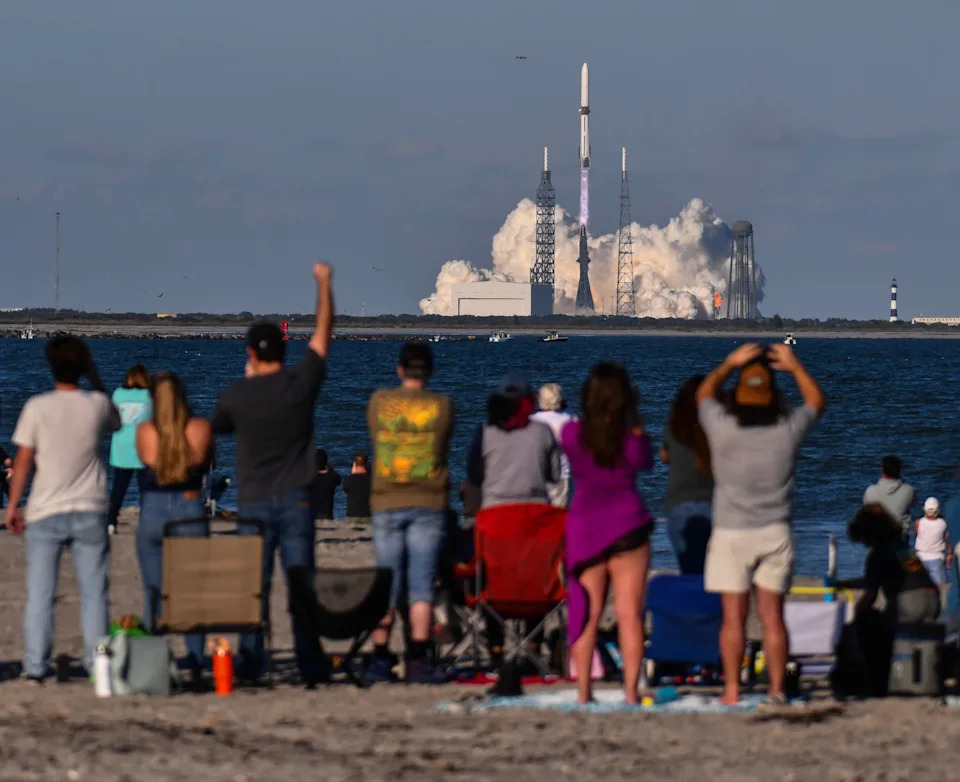
This photo depicts a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket carrying the latest batch of Amazon's broadband satellites on Dec. 16 to low-Earth orbit after launching from the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Formerly called Project Kuiper, the venture has since been renamed Amazon Leo. Since its debut April launch, Amazon Leo has deployed 180 of 3,000 satellites planned for its first constellation, which could challenge SpaceX's Starlink.
A group of Blue Origin employees with their friends and families gather on the beach in Cape Canaveral for the launch of Blue Origin's second New Glenn rocket in 2025. Following its January debut, the rocket launched for the second time Nov. 13 from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, sending NASA's twin ESCAPADE spacecraft on their trek to Mars.
Darkness falls Nov. 9 as a Blue Origin New Glenn rocket is prepped for its second-ever launch from the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. Blue Origin is developing the towering rocket for heavy-lift missions that could see Jeff Bezos' company compete with Elon Musk and SpaceX.
The SpaceX Starship spacecraft sits Oct. 12, 2025 atop the Super Heavy booster before sunrise as preparations continue for its 11th test flight from the company's complex in Starbase, Texas.
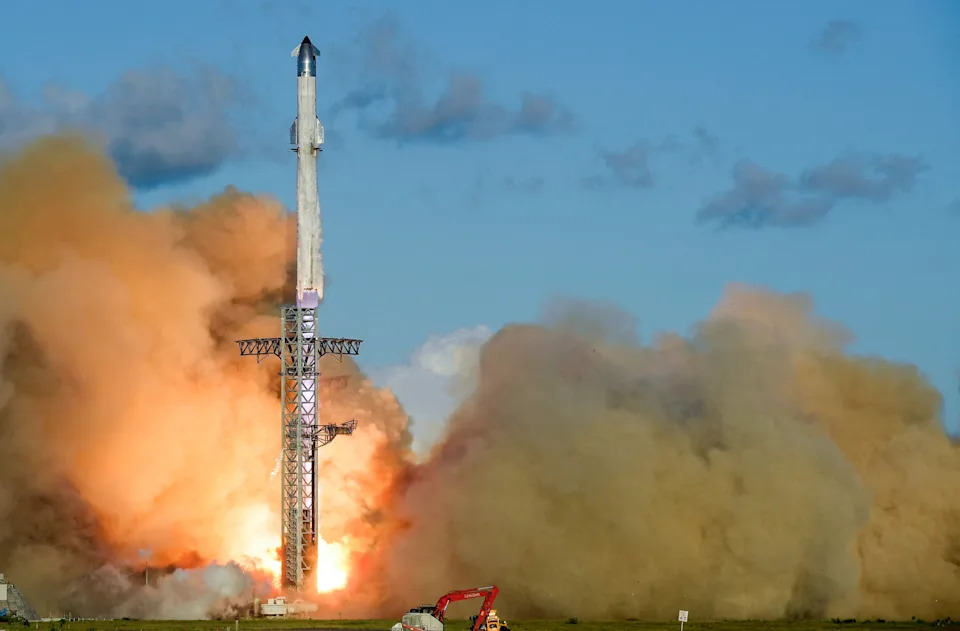
A SpaceX Super Heavy booster carrying the Starship spacecraft lifts off Oct. 13, 2025, on its 11th ever test flight at the company's launch pad in Starbase, Texas. The launch was Starship's fifth of 2025, and second consecutive successful test flight following a year that was early on marked by explosive failures. SpaceX is developing the rocket for future missions that would help NASA astronauts land on the moon and also potentially transport the first humans to Mars.
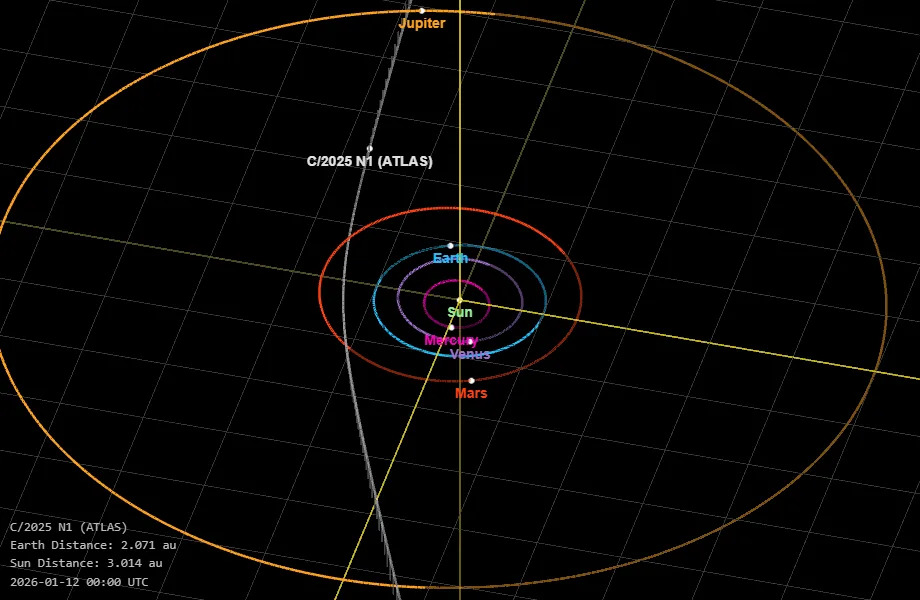
Here's a look at 3I/ATLAS's location in the solar system as of Jan. 12, 2026.
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope last observed come 3I/ATLAS on Nov. 30, about four months after Hubble's first look at the interstellar comet. 3I/ATLAS became one of the biggest cosmic stories of the year when astronomers deemed it to be the third-ever discovered interstellar object in our solar system originating from an entirely different part of the galaxy.
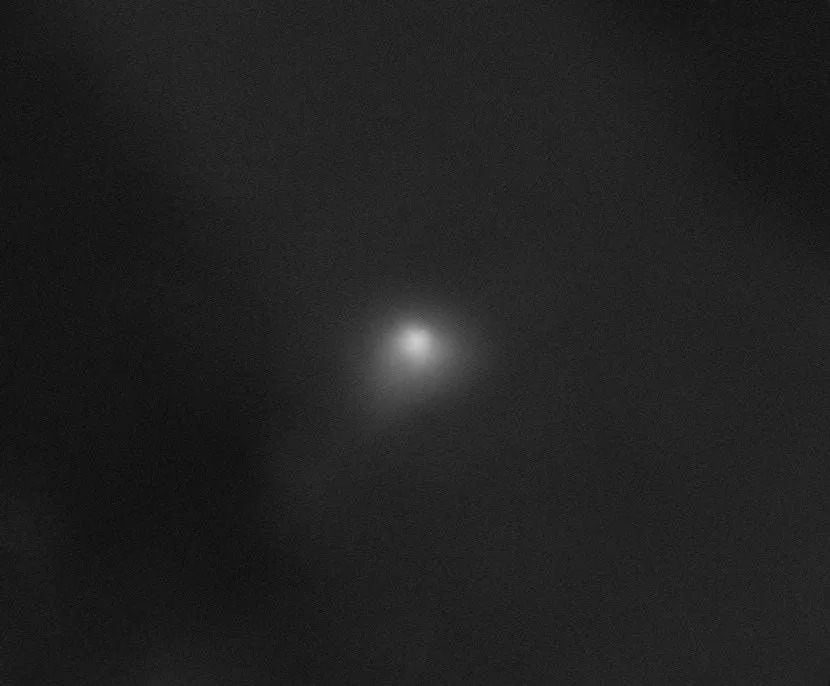
The High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera aboard NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter captured this image of interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS on Oct. 2, 2025. At the time it was imaged, the comet was about 19 million miles from the spacecraft. The comet didn't come nearly as close to Earth, when it reached a distance of 170 million miles from our planet on Dec. 19.
This image shows the 3I/ATLAS interstellar comet as a bright, fuzzy orb in the center. Traveling through our solar system at 130,000 miles per hour, 3I/ATLAS was made visible by using a series of colorized stacked images from Sept. 11-25, using the Heliocentric Imager-1 (H1) instrument, a visible-light imager on the STEREO-A (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) spacecraft. The colorization was applied to differentiate the image from other observing spacecraft images.
Because it's big enough to be deemed a "city killer," asteroid 2024 YR4 became a source of alarm due to the uncommonly high risk it had of colliding with Earth on Dec. 22, 2032. For a time, it was the only object among more than 37,000 known large space rocks with any chance of hitting Earth anytime soon – with its probability of impact even rising to a record level of 3.1%.That began to change in late February as more precise observations allowed scientists to effectively winnow down the asteroid's odds of impact to a number so low, it might as well be zero.
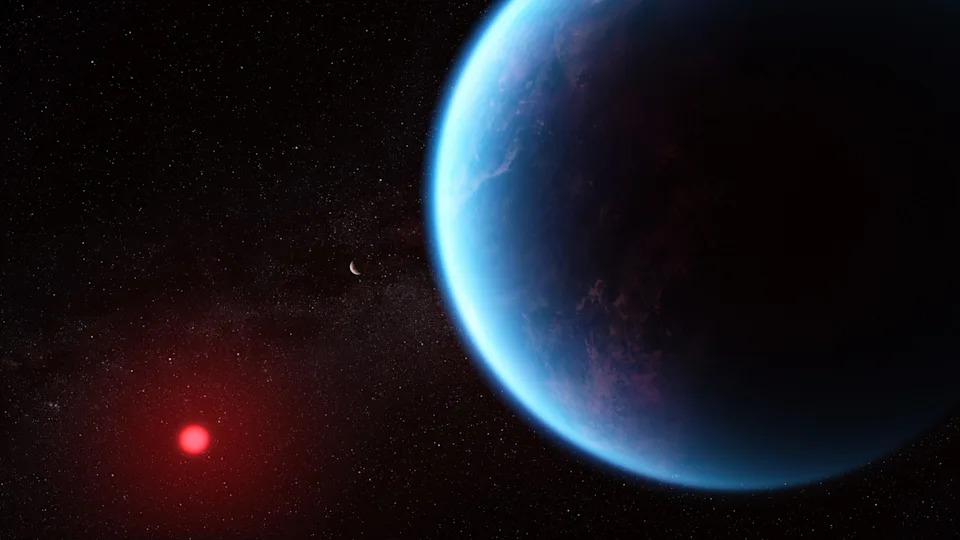
An exoplanet known as K2-18b achieved a degree of fame in April when a team of astronomers claimed to have found in its atmosphere "the strongest evidence yet" that life exists anywhere else besides Earth. Other scientists have since cast doubt on the findings – putting a damper on the notion that humanity finally had proof that we aren't alone in the cosmos.
This artist's concept shows what exoplanet K2-18b could look like based on scientific data. NASA's James Webb Space Telescope has observed K2-18b, an exoplanet 8.6 times as massive as Earth, revealing conditions that could support life on the exoplanet.
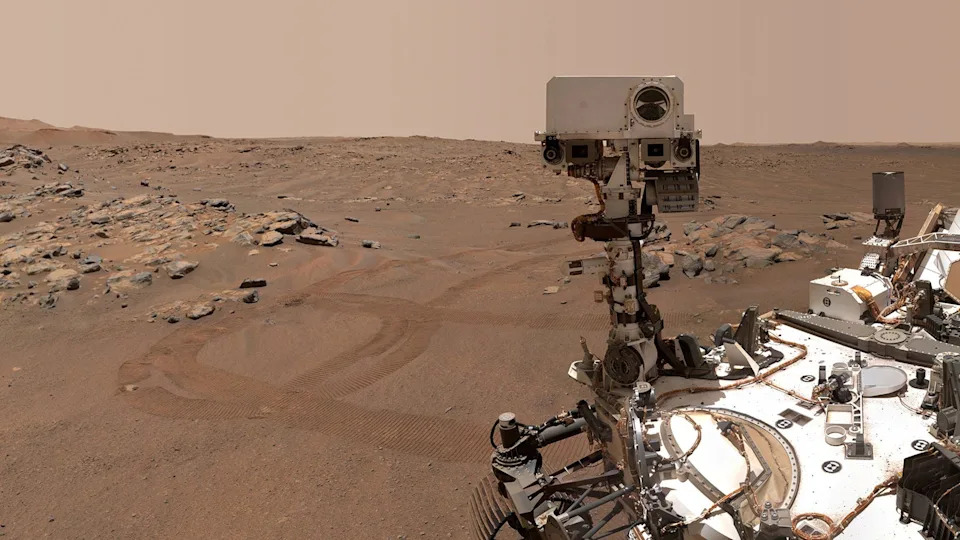
NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover is seen in a "selfie" that it took over on Sept. 10, 2021. Perseverance rover, along with Curiosity, is one of the agency's two car-sized robots exploring the Martian surface for signs that the planet was once habitable. And in September, NASA officials confirmed that one of the rovers’ finds contained a potential biosignature.
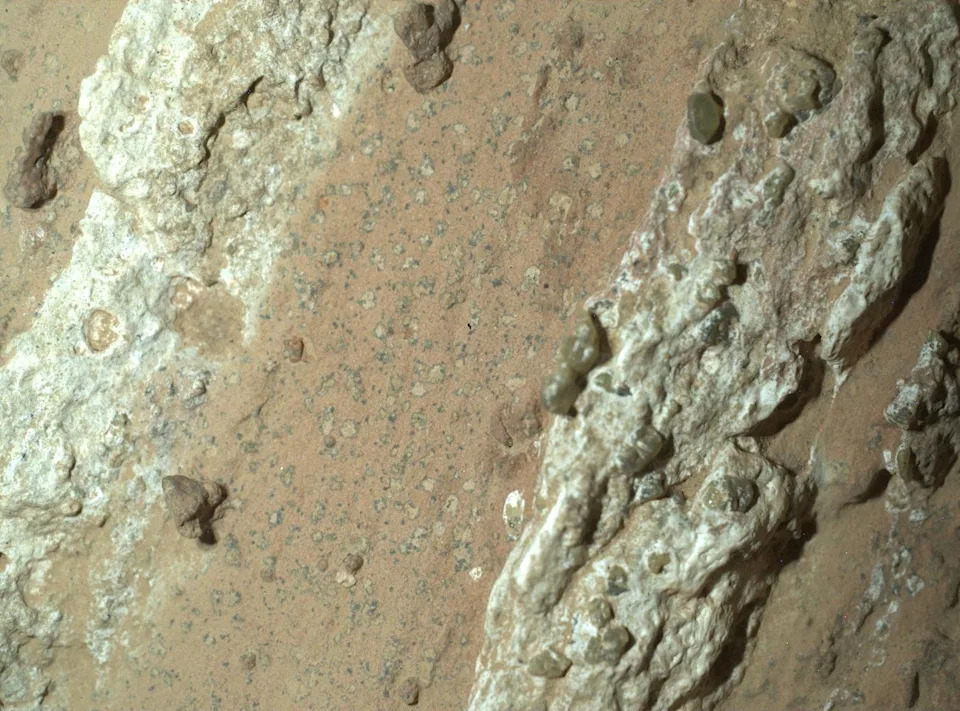
A reddish rock nicknamed "Cheyava Falls", with features resembling leopard spots was discovered by NASA's Perseverance rover in Mars’ Jezero Crater in July 2024, in this handout photograph released on September 10, 2025.
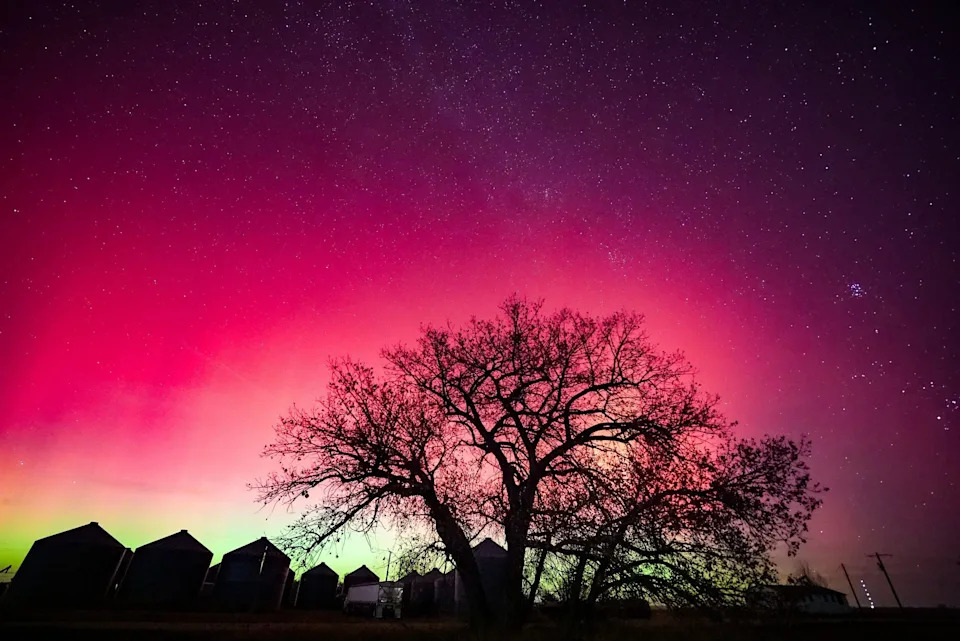
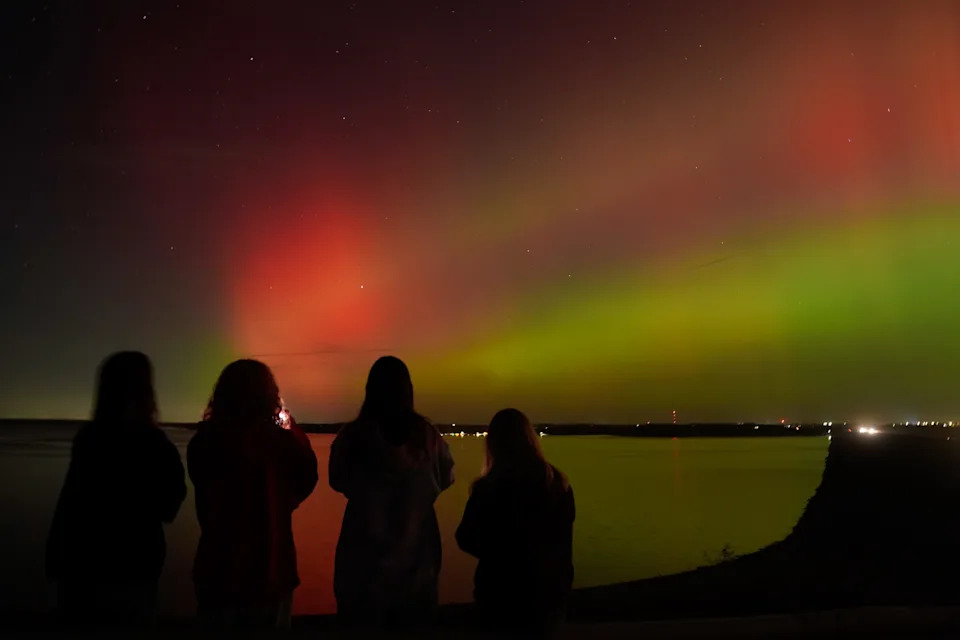
The northern lights, also known as the aurora borealis, light up the night sky Nov. 11 east of Denver, Colorado. A powerful geomagnetic solar storm in November blasted Earth and created the conditions necessary to reveal the auroras much further south in the United States than is typical.
A group of friends take photos of the northern lights Nov. 11 as they appear over Clinton Lake in Lawrence, Kansas. After NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center issued a "severe" geomagnetic storm watch in November, many people in the Northern Hemisphere, which includes the U.S., had an extraordinary opportunity to gaze upon some breathtaking red and green auroras in their own backyard.
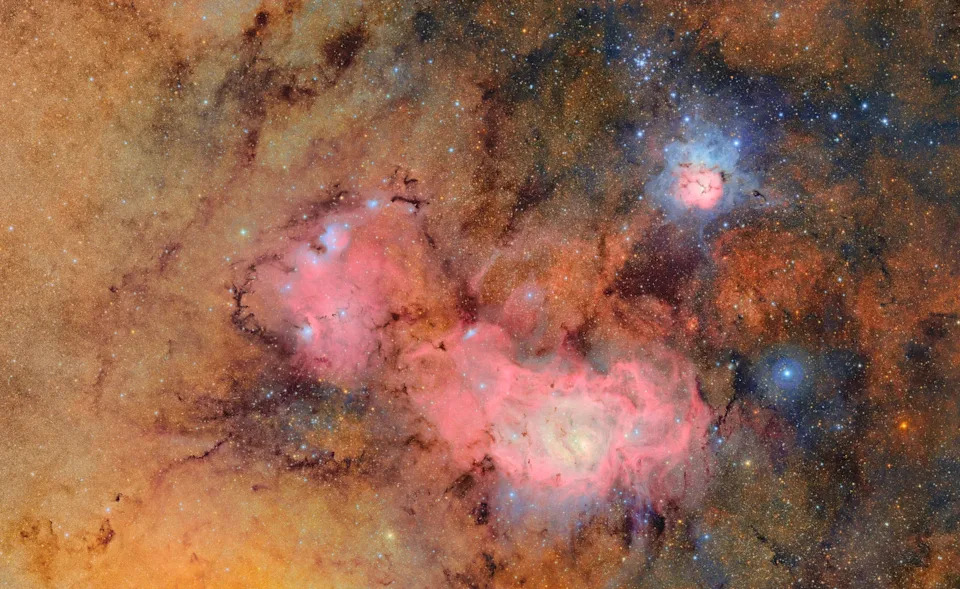
In June, the state-of-the-art Vera C. Rubin ground telescope in Chile unveiled its first stunning images of the cosmos. This particular image combines 678 separate images taken by the observatory in just over seven hours of observing time. Combining many images in this way clearly reveals otherwise faint or invisible details, such as the clouds of gas and dust that comprise the Trifid nebula (top) and the Lagoon nebula, which are several thousand light-years away from Earth.
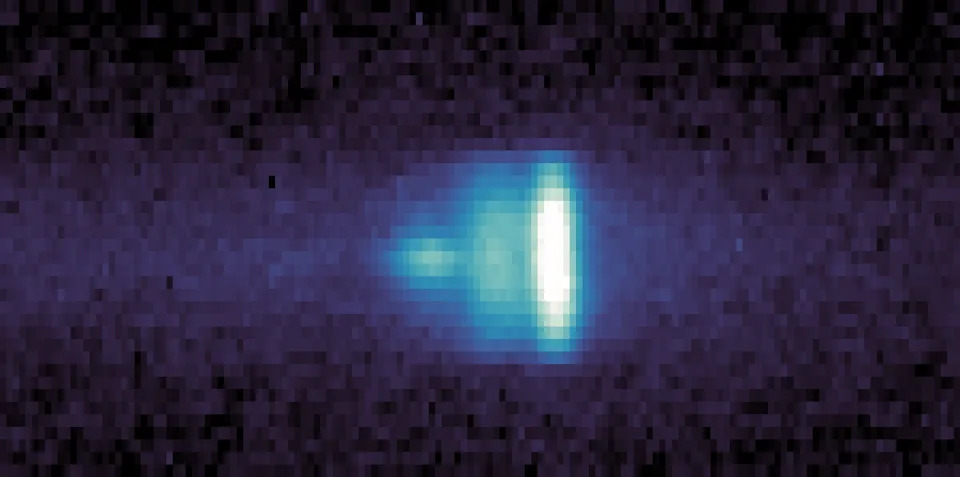
NASA’s Psyche mission acquired four observations of interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS over the course of eight hours on Sept. 8 and 9, 2025, when the comet was about 33 million miles from the spacecraft. The data, captured by Psyche’s multispectral imager, is helping astronomers both refine the trajectory of 3I/ATLAS and learn more about the faint coma, or cloud of gas, surrounding its nucleus.
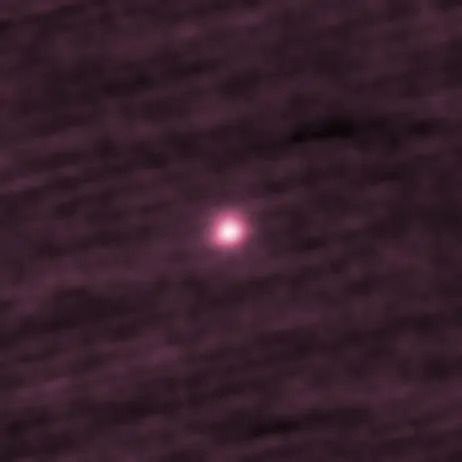
This image shows the observation of comet 3I/ATLAS when it was discovered on July 1, 2025. The NASA-funded ATLAS survey telescope in Chile first reported that the comet originated from interstellar space.
A faint image of comet 3I/ATLAS as observed by ESA/NASA’s SOHO mission between Oct. 15-26, 2025. The comet appears as a slight brightening in the center of the image.
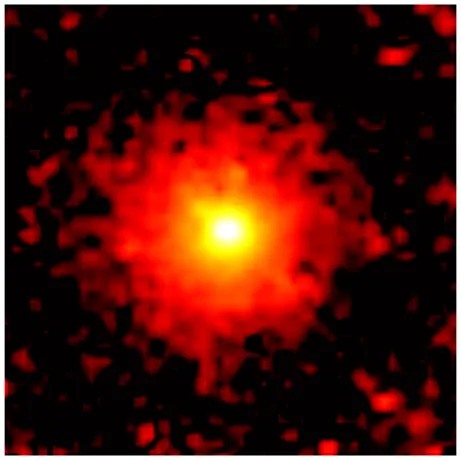
This image shows the halo of gas and dust, or coma, surrounding comet 3I/ATLAS, the third interstellar object ever detected by astronomers as it passes through our solar system. The image was taken on Oct. 9, 2025, by an instrument onboard NASA's MAVEN spacecraft, which has been studying Mars from its orbit since 2014. The instrument, the Imaging Ultraviolet Spectrograph, takes pictures in the ultraviolet part of the spectrum to reveal the chemical composition of objects.
An ultraviolet image composite of the hydrogen atoms surrounding comet 3I/ATLAS, the third interstellar object ever detected by astronomers, as it passes through our solar system. This image was taken on Sept. 28, just days before the comet’s closest approach to Mars - by an instrument on NASA's MAVEN spacecraft, which has been studying Mars from orbit since 2014.
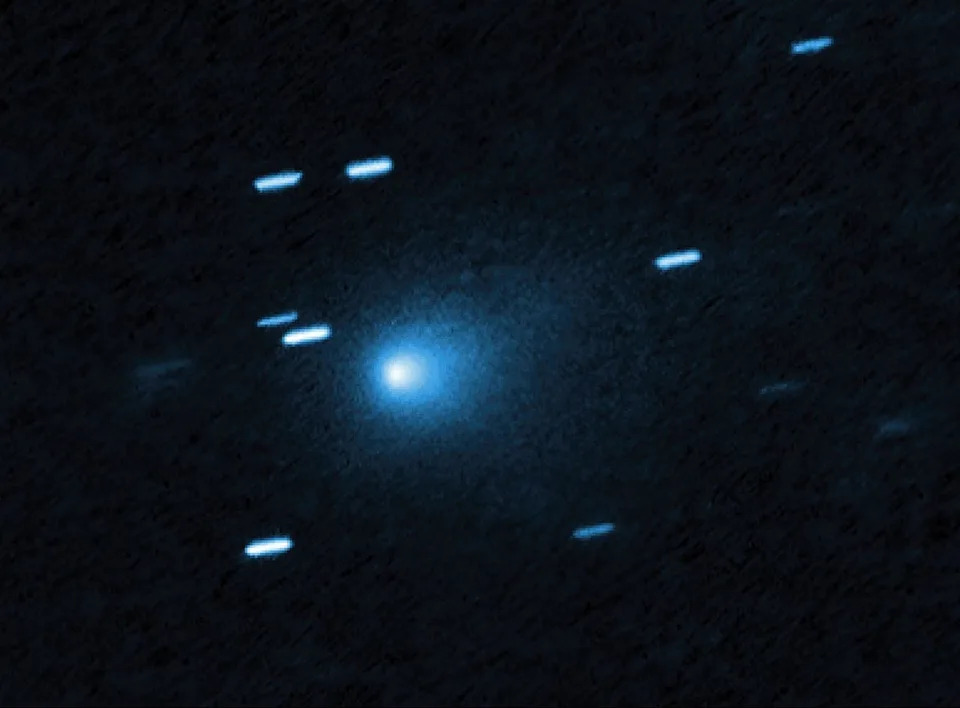
Comet 3I/ATLAS appears as a bright object near the center of this image, made from combining observations from NASA’s PUNCH mission taken from Sept. 20 to Oct. 3, 2025, when the comet was about 231 million to 235 million miles from Earth. Its tail appears as a short elongation to the right. Stars appear as streaks in the background.
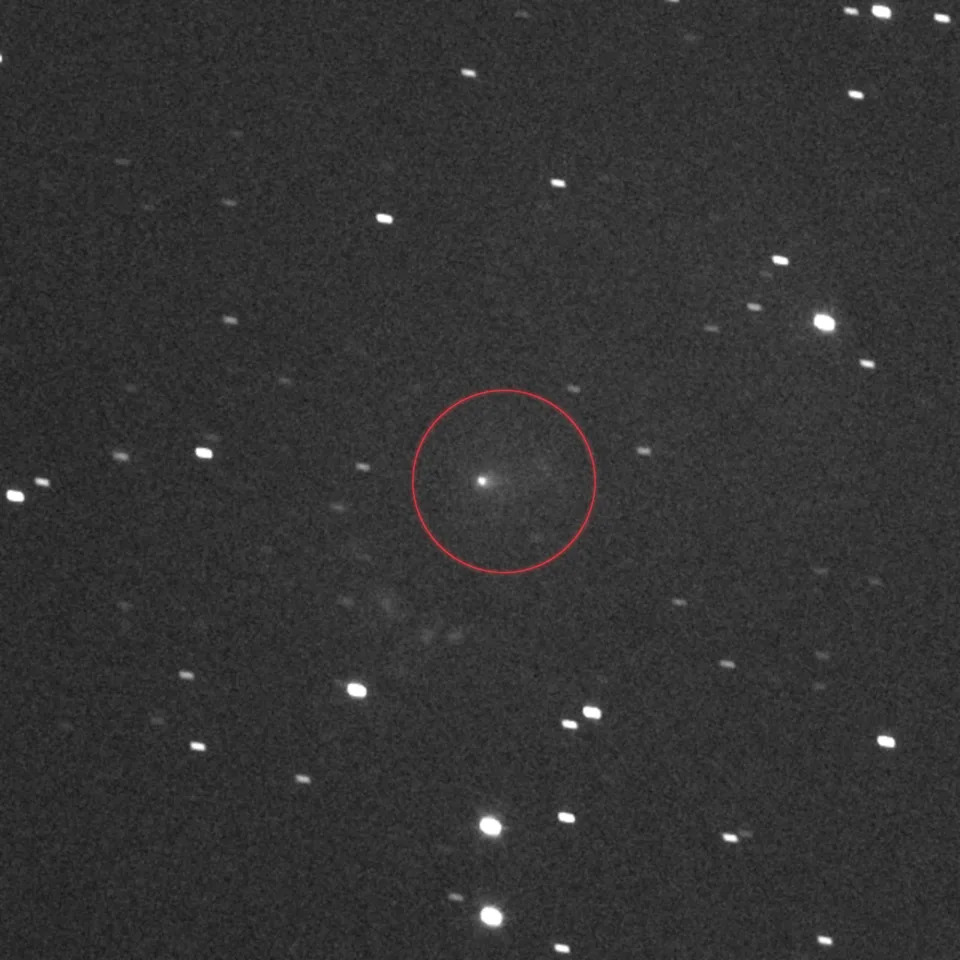
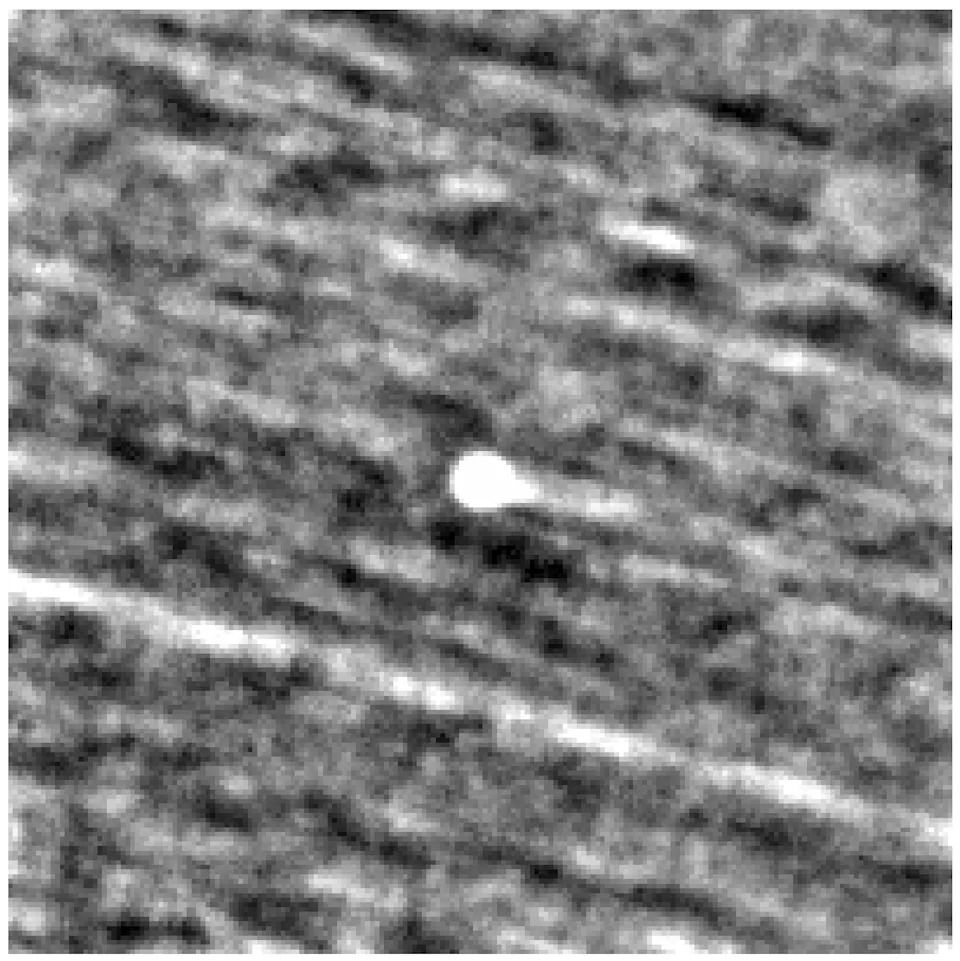
The interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS, circled in the center, as seen by the L’LORRI panchromatic, or black-and-white, imager on NASA’s Lucy spacecraft. This image was made by stacking a series of images taken on Sept. 16, as the comet was zooming toward Mars. Lucy was 240 million miles away from 3I/ATLAS at the time making its way to explore eight asteroids that share an orbit with Jupiter.
NASA’s SPHEREx space telescope observed interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS from Aug. 7 to Aug. 15.
Hubble captured this image of the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS on July 21, 2025, when the comet was 277 million miles from Earth. Hubble shows that the comet has a teardrop-shaped cocoon of dust coming off its solid, icy nucleus.
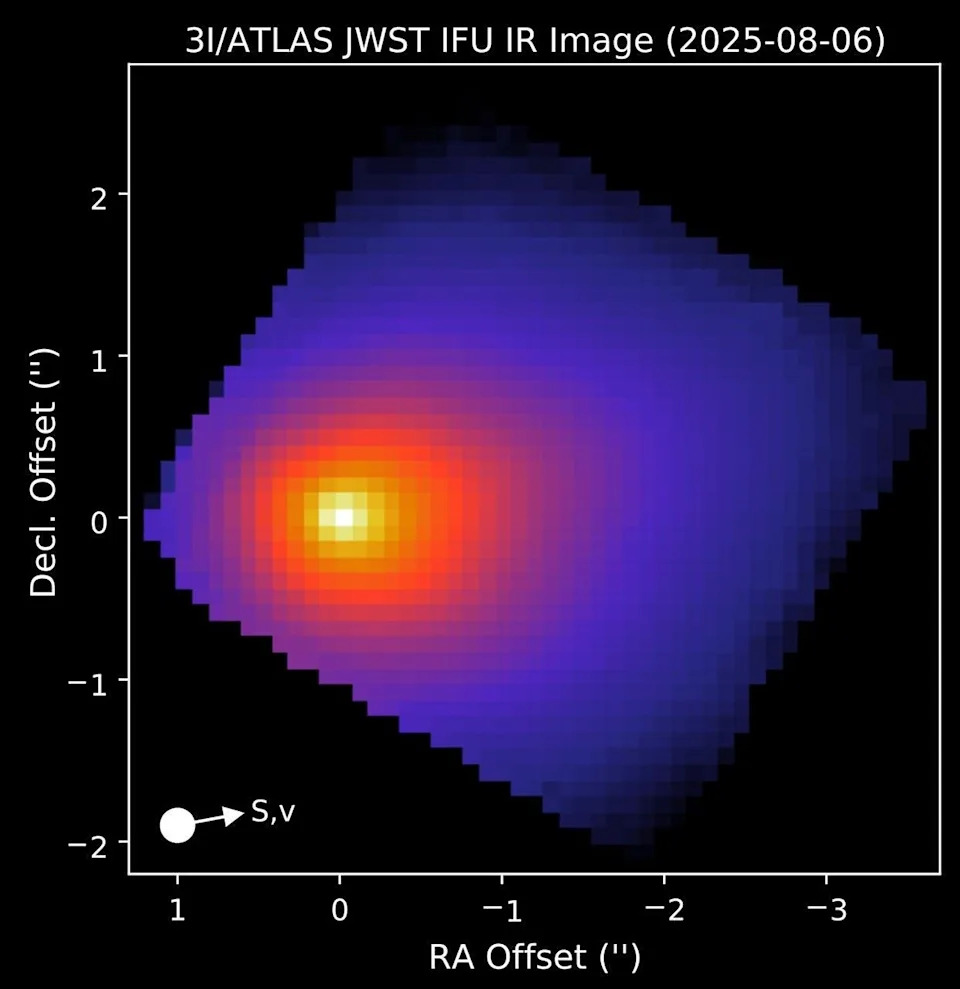
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope observed interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS Aug. 6, with its Near-Infrared Spectrograph instrument