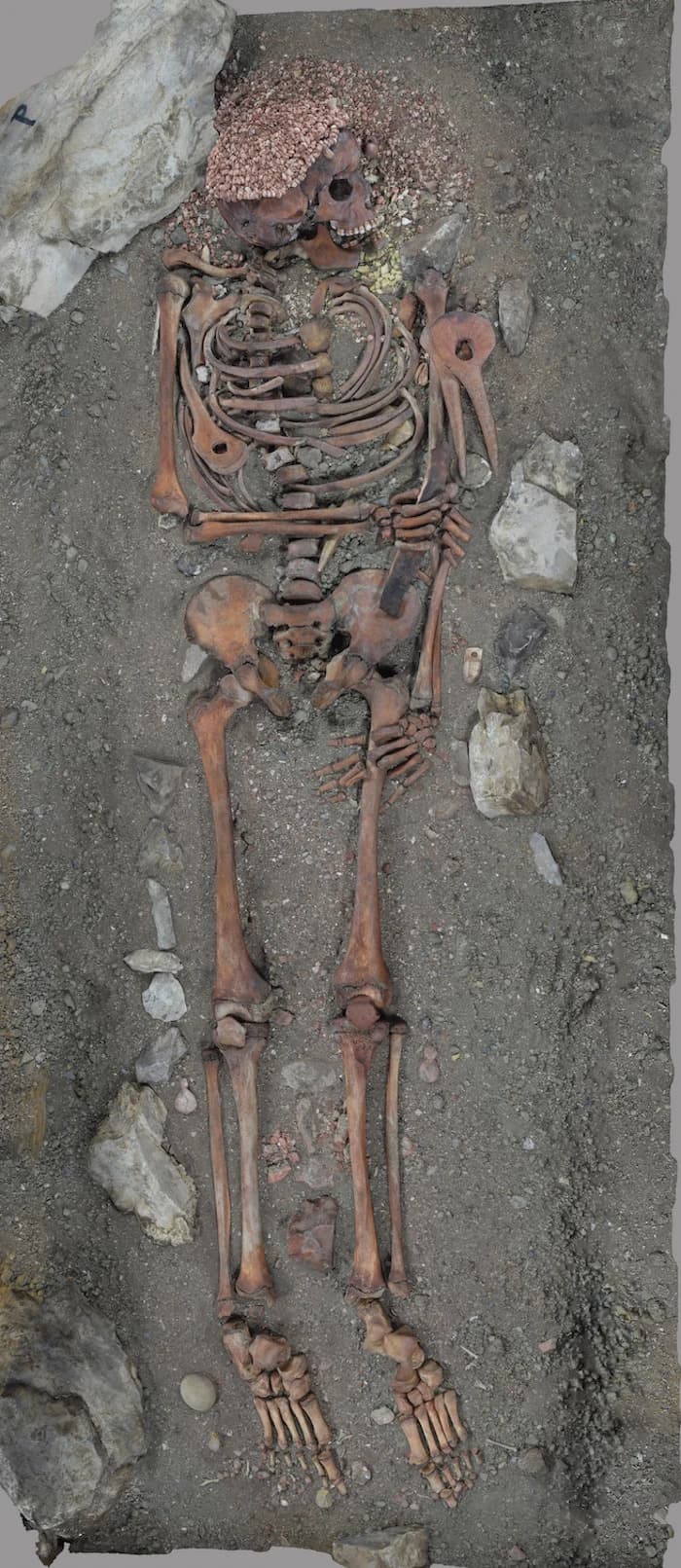
Neanderthal sites show burials, arranged skulls, rock art, engraved bones, feather use and modified talons — behaviors that suggest ritual or symbolic activity. Some researchers, like Patrick McNamara, interpret these patterns as shamanic or religious practices, including possible animal veneration and ritual cannibalism. Others, including Robin Dunbar and Margaret Boone Rappaport, argue Neanderthals may have had intense spiritual experiences but lacked the neurocognitive complexity for modern theological systems. The evidence is compelling but ambiguous, and the question remains open.
Did Neanderthals Have Religion? What the Archaeological Evidence Suggests

Neanderthals, who disappeared more than 30,000 years ago, left traces of behavior that many researchers interpret as ritualized or symbolic. While some finds hint at spiritual practices, scholars disagree over whether these behaviors amount to what we would call religion.
Evidence of ritualized behavior
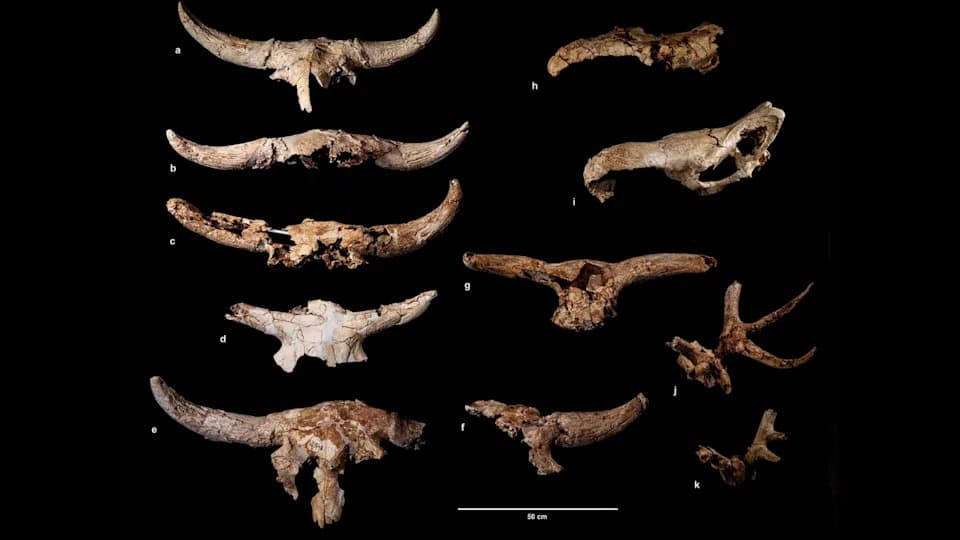
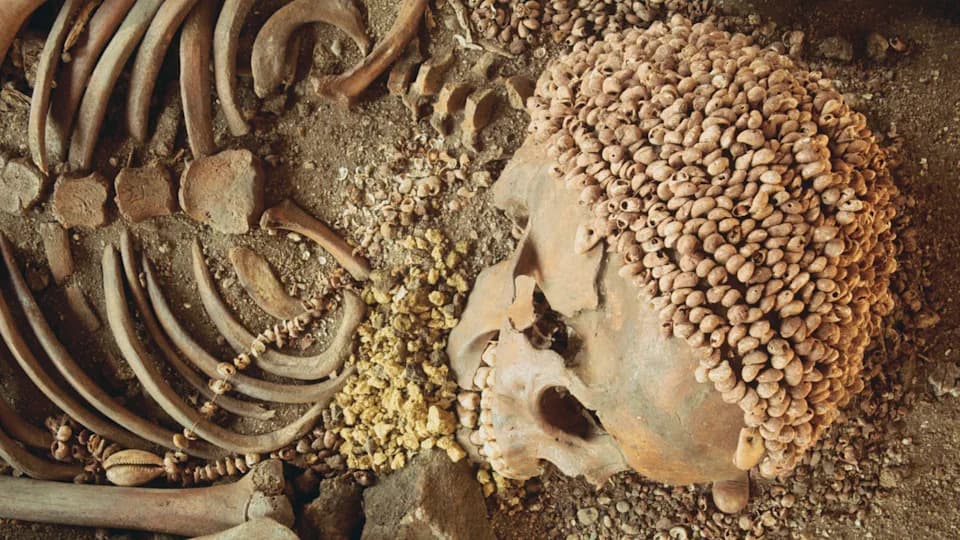
Archaeological sites attributed to Neanderthals include deliberate burials, arrangements of animal skulls in caves, rock art and engravings on bones, the removal of bird feathers (perhaps for decoration), and the modification or use of eagle talons that could have been worn as pendants. There is also evidence of cannibalism at some sites, which has been interpreted by some researchers as potentially ritual in nature.
How researchers interpret the evidence
Experts offer a range of interpretations. Patrick McNamara, a neurologist who studies the evolution of religious experience, argues that some Neanderthal behaviors resemble shamanic practice: ritual burials, cave-focused activities, arranged skulls that resemble altars, and what he calls "bear ceremonialism" in which bear skulls appear to have been intentionally displayed. McNamara suggests these patterns point to ritual action directed at supernatural agents or powers.
Other scholars urge a more cautious reading. Robin Dunbar, emeritus professor of evolutionary psychology at the University of Oxford, accepts that Neanderthals likely had powerful experiences of awe, mystery and engagement with their world but doubts they held organized theological beliefs comparable to modern religions. Margaret Boone Rappaport, an anthropologist who researches religion's emergence, likewise suggests Neanderthals may have performed rituals without possessing the advanced neurocognitive architecture for complex theological thought. She and others point to differences in brain structure — notably less expansion of regions such as the precuneus, which is implicated in imagining agents and complex social cognition — as potentially limiting the development of formalized theologies.
Karel Kuipers, an archaeologist at Leiden University, emphasizes interpretive caution: behaviors we now associate with ritual, like burial, could have served practical purposes (for example, removing a decomposing body from a living area) rather than expressing spiritual beliefs. The archaeological record is fragmentary, and context matters: the same physical traces can have multiple plausible meanings.
Where the evidence leaves us
Overall, the record shows that Neanderthals engaged in behaviors that look ritualized and symbolic. Whether these behaviors reflect religious systems with beliefs in supernatural beings, or instead represent episodic spiritual experiences, social practices, or pragmatic actions, remains unresolved. Current opinion ranges from interpretations that see shaman-like ritual and animal veneration to more conservative views that acknowledge meaningful experiences without concluding the presence of full theological religions. Future discoveries and refined analyses of context, wear patterns, and comparative neuroscience will continue to shape this debate.
Bottom line: Neanderthals clearly practiced behaviors with ritual qualities, but whether they had religion in the human sense of organized supernatural beliefs is still an open question.
Help us improve.