President Trump reiterated plans to pursue Greenland, calling it vital to U.S. power and citing national-security and personal reasons. European leaders and Greenlandic officials strongly oppose the proposal, and polls show about 85% of Greenlanders oppose joining the U.S. Greenland’s vast size (836,330 sq miles), Arctic position, northern military facilities and significant mineral deposits — increasingly exposed by melting ice — explain why the island is central to rising geopolitical competition.
Why Trump Pushed To Annex Greenland: Strategy, Resources and Global Stakes

President Donald Trump reiterated early Tuesday that there is "no going back" on his push to bring Greenland into the United States, doubling down on a proposal that has drawn strong condemnation from Greenlandic leaders and key European officials.
On Truth Social, Mr. Trump wrote: "The United States of America is the most powerful Country anywhere on the Globe, by far. We are the only POWER that can ensure PEACE throughout the World." He also posted an image that appears to show a private text from French President Emmanuel Macron expressing bewilderment about Mr. Trump’s intentions toward Greenland.

Diplomatic Pushback
At the World Economic Forum in Davos, President Macron warned that threats to seize territory "one way or the other" risk undermining international law. "We’re shifting to a world without rules ... where international law is trampled underfoot, and where the only law that seems to matter is that of the strongest," he said, calling attention to the wider implications of any attempt to annex sovereign territory.
Legal Status And Local Opinion
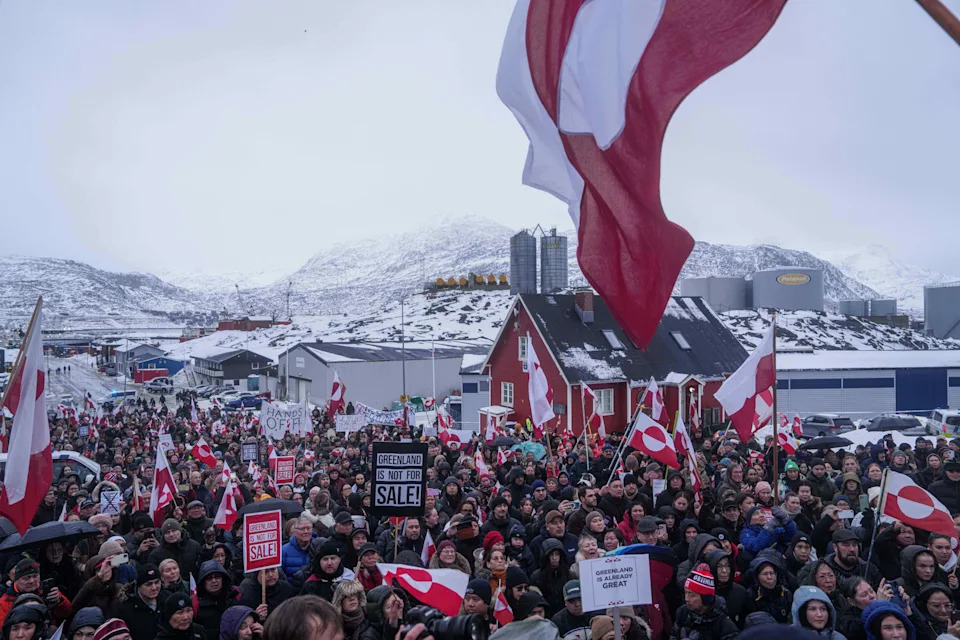
Greenland is part of the Kingdom of Denmark but exercises broad self-rule over internal affairs. Greenlanders have the legal right to decide their political future — including remaining within the Danish realm, seeking independence, or exploring other arrangements — and recent polling shows roughly 85% oppose joining the United States. The territory’s government has been emphatic that "Greenland is not for sale," and many island residents view external acquisition efforts as a threat to their autonomy.
Why Greenland Matters
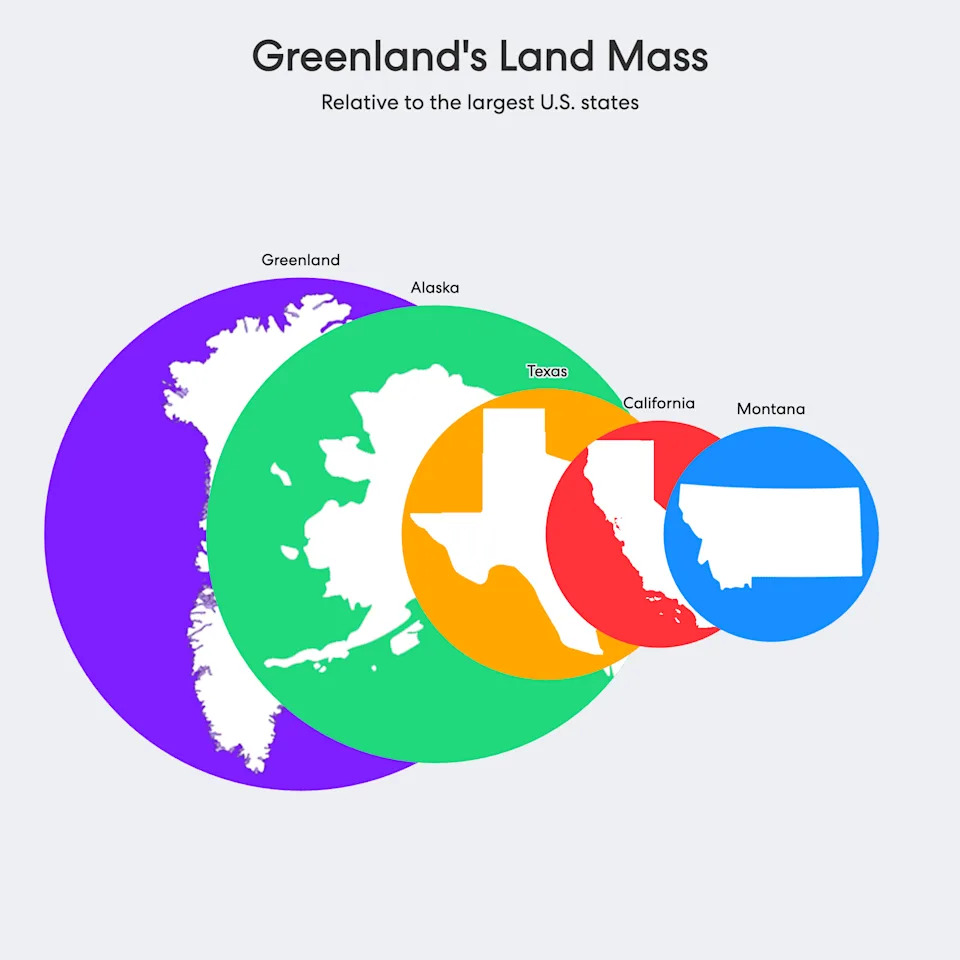
Beyond politics and headlines, Greenland’s significance is geographic, military and economic. The island spans about 836,330 square miles — more than three times the size of Texas — with roughly 56,000 residents concentrated along the coasts. Its remote, icy interior is sparsely inhabited.
Strategic Location
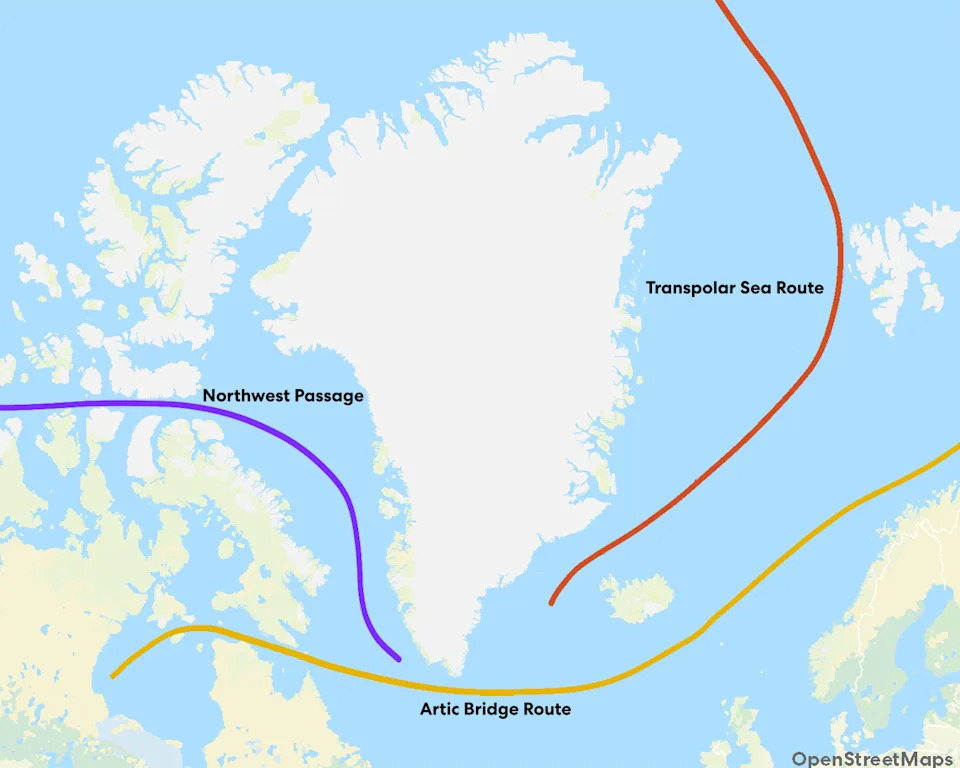
Major Arctic and North Atlantic sea lanes run along Greenland’s coasts, including routes near the fabled Northwest Passage and the so-called Arctic Bridge between northern Europe and North America. Greenland also hosts a U.S. military presence at a long-standing northern base (Thule area installations), giving the United States forward access for missile-warning and early-warning systems.
Climate And Resources
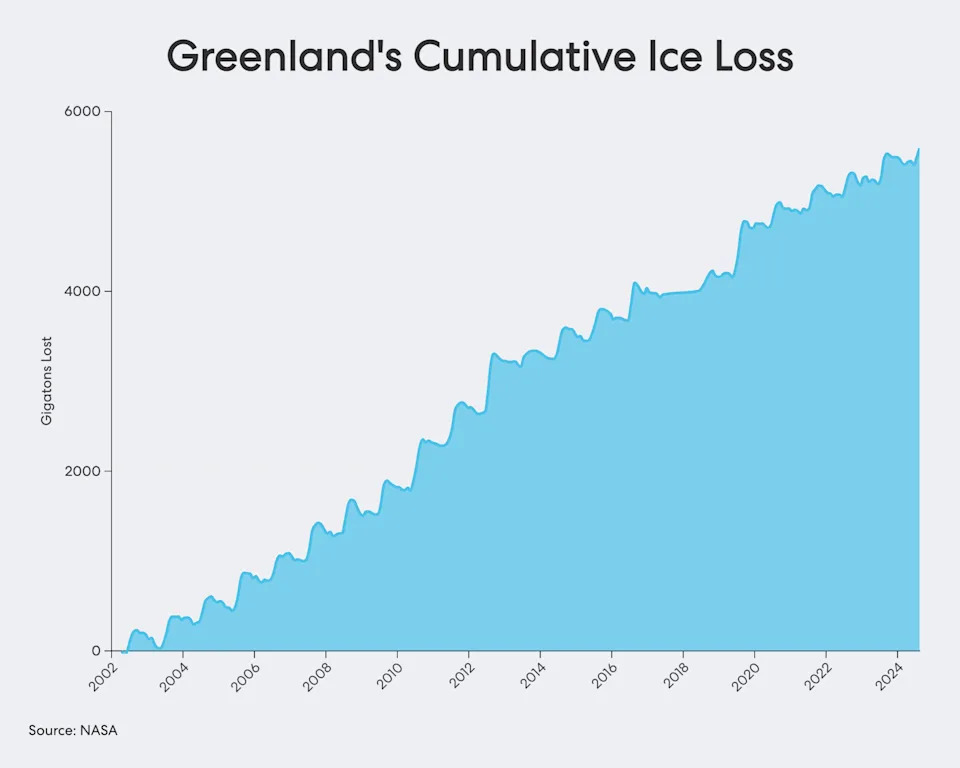
Climate change is rapidly reshaping the Arctic. Scientists estimate Greenland has lost roughly 2,000 square miles of surface ice over the past four decades, a change that contributes to sea-level rise and can influence major ocean currents. Melting ice also exposes previously inaccessible deposits of rare earth elements and other critical minerals used in electronics, defense and clean-energy technologies.
While Greenland currently enforces strict mining regulations and bans oil and gas extraction for environmental reasons, receding ice has intensified interest in the island’s mineral potential. However, harsh weather, rugged terrain and high costs have historically limited large-scale extraction — and many experts caution that mineral development may remain technically and economically challenging.
Geopolitical Stakes
Sovereignty over Greenland would carry major geopolitical implications. Control of the island would strengthen a state’s Arctic posture and influence over emerging northern shipping lanes, while also touching on sensitive issues of international law, indigenous rights and environmental protection. The United States, Russia, China and NATO countries are all increasingly attentive to Arctic dynamics as climate change opens new possibilities and strategic competition intensifies.
Whatever the motives driving Mr. Trump’s statements — strategic, economic or personal — the conversation around Greenland highlights how geography, climate and resources intersect with modern geopolitics.
Help us improve.


































